library(sf)Linking to GEOS 3.10.2, GDAL 3.4.1, PROJ 8.2.1; sf_use_s2() is TRUElibrary(stars)Loading required package: abindPart 4: Extracting from mesh
library(sf)Linking to GEOS 3.10.2, GDAL 3.4.1, PROJ 8.2.1; sf_use_s2() is TRUElibrary(stars)Loading required package: abindImporting the points:
pnt = st_read('data/export/Address coordinates.gpkg')Reading layer `extracted' from data source
`/home/michael/Sync/presentations/p_2023_01_R_exposure_tutorial/data/export/Address coordinates.gpkg'
using driver `GPKG'
Simple feature collection with 13710 features and 2 fields
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 669825 ymin: 6578850 xmax: 695023 ymax: 6590699
Projected CRS: SWEREF99 TMpntSimple feature collection with 13710 features and 2 fields
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 669825 ymin: 6578850 xmax: 695023 ymax: 6590699
Projected CRS: SWEREF99 TM
First 10 features:
X_sw99_corr_final Y_sw99_corr_final geom
1 6579476 672969 POINT (672969 6579476)
2 6579535 672998 POINT (672998 6579535)
3 6580754 673589 POINT (673589 6580754)
4 6580685 670730 POINT (670730 6580685)
5 6580685 670730 POINT (670730 6580685)
6 6580707 670681 POINT (670681 6580707)
7 6580685 670730 POINT (670730 6580685)
8 6580063 671015 POINT (671015 6580063)
9 6581347 672437 POINT (672437 6581347)
10 6582407 673401 POINT (673401 6582407)plot(st_geometry(pnt))
Conversion from mesh (.2dm) to GeoTIFF (.tif) can be done using the QGIS tool named native:meshrasterize, from within R:
x = 'qgis_process run native:meshrasterize -- INPUT="data/export/Noise/Road traffic/Road_traffic_noise_2018_L_PF.2dm" DATASET_GROUPS="0" DATASET_TIME="2022-01-15" PIXEL_SIZE="20" OUTPUT="tmp.tif"'
system(x)or from the command line:
export QT_QPA_PLATFORM="offscreen"
qgis_process run native:meshrasterize -- INPUT="data/export/Noise/Road traffic/Road_traffic_noise_2018_L_PF.2dm" DATASET_GROUPS="0" DATASET_TIME="2022-01-15" PIXEL_SIZE="20" OUTPUT="tmp.tif"
qgis_processThe raster file we got from qgis_process can be imported back into the R environment:
r = read_stars('tmp.tif')
names(r) = 'traffic_noise'
rstars object with 2 dimensions and 1 attribute
attribute(s):
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
traffic_noise 15.097 26.694 40.307 39.88116 52.746 75
dimension(s):
from to offset delta refsys point values x/y
x 1 1262 669825 20.0079 NA NA NULL [x]
y 1 592 6590700 -20.0169 NA NA NULL [y]In this case the CRS definition is missing:
st_crs(r)Coordinate Reference System: NAWe can set it as follows, based on prior knowledge that the raster CRS is the same as the points layer CRS:
st_crs(r) = st_crs(pnt)
rstars object with 2 dimensions and 1 attribute
attribute(s):
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
traffic_noise 15.097 26.694 40.307 39.88116 52.746 75
dimension(s):
from to offset delta refsys point values x/y
x 1 1262 669825 20.0079 SWEREF99 TM NA NULL [x]
y 1 592 6590700 -20.0169 SWEREF99 TM NA NULL [y]plot(r, col = hcl.colors(11, 'Spectral', rev = TRUE), reset = FALSE)
plot(st_geometry(pnt), add = TRUE)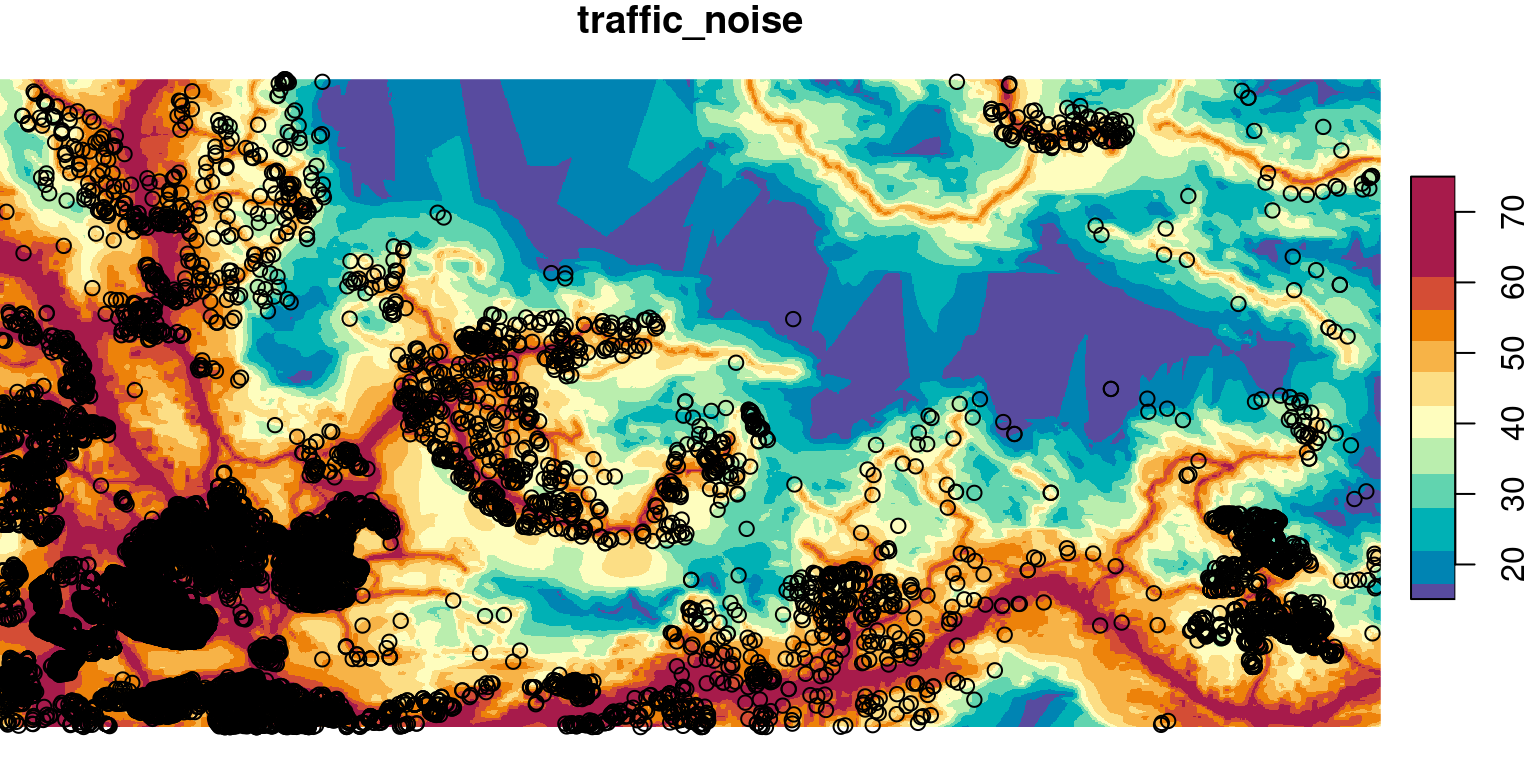
Now the raster values can be extracted to points using st_extract as shown previously (see Part 1):
pnt$traffic_noise = st_extract(r, pnt)[[1]]
pntSimple feature collection with 13710 features and 3 fields
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 669825 ymin: 6578850 xmax: 695023 ymax: 6590699
Projected CRS: SWEREF99 TM
First 10 features:
X_sw99_corr_final Y_sw99_corr_final geom traffic_noise
1 6579476 672969 POINT (672969 6579476) 57.981
2 6579535 672998 POINT (672998 6579535) 55.749
3 6580754 673589 POINT (673589 6580754) 61.455
4 6580685 670730 POINT (670730 6580685) 63.560
5 6580685 670730 POINT (670730 6580685) 63.560
6 6580707 670681 POINT (670681 6580707) 64.200
7 6580685 670730 POINT (670730 6580685) 63.560
8 6580063 671015 POINT (671015 6580063) 64.197
9 6581347 672437 POINT (672437 6581347) 63.831
10 6582407 673401 POINT (673401 6582407) 57.880plot(pnt['traffic_noise'])