General information#
Last updated: 2025-02-04 09:32:46
Course details#
Course number: 128.1.0162
Time: Sunday 16:10-19:00
Place: Building 72, room 481
Instructor: Michael Dorman (dorman@post.bgu.ac.il)
Grading:
Home assignments 4 * 12.5% = 50% (see Home assignments)
Exam = 50% (see Exam)
Requirements:
Basic knowledge of GIS (e.g., “Intro to GIS” course)
Self study
Getting help:
Forum on Moodle (http://moodle2.bgu.ac.il)
Meetings (schedule by e-mail)
Lecture plan#
The course lecture plan is given in Table 29.
Home assignments#
Submission dates#
The sumbission dates of home assignments are given in Table 30.
Assignment |
Topic(s) |
Date |
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
Instructions#
Assignments should be prepared and submitted individually (not in pairs, etc.)
The solution needs to be submitted on Moodle, as a Jupyter notebook (i.e., a single
.ipynbfile).Use markdown cells or code comments to specify (Fig. 83) the following details at the top of the notebook:
Assignment number
Student name
Student ID
Use
## Question 1and## Question 2in markdown cells to create headings marking the solution to question 1 and question 2 (Fig. 83).The notebook needs to run without errors, and produce (print) the required outputs, assuming the person who runs the notebook:
Has all packages used in the book installed (see Python packages).
Runs the notebook from within a directory that contains the
dataandoutputsub-directories, with the course sample data and output files (see Sample data).
Avoid exporting any files in your code!
Make sure your solution is as general as possible. Namely, do not use indices or specific values in your solution, other than the values given in the question text. For example, if the question is “find the largest value in the list
x=[4,7,9,2,8,5], the solutionx[2]is wrong, because it uses the specific value2.You can use any function or method in the Python standard library (https://docs.python.org/3/library/) to solve the exercises, even if it is not in the material. However, you can only use third-party Python packages which are covered in the material (see What are we going to learn?); you cannot use any other third-party package in your solution.
When the solution requires importing one of the sample data or output files (see Sample data), use a relative path
strstarting with'data'or'output', and use/(!) as the separating character, as in'data/carmel.csv'. That way, you assume that the notebook is going to be executed in a a directory which contains a sub-directory nameddatawith all sample data files listed in Table 3.
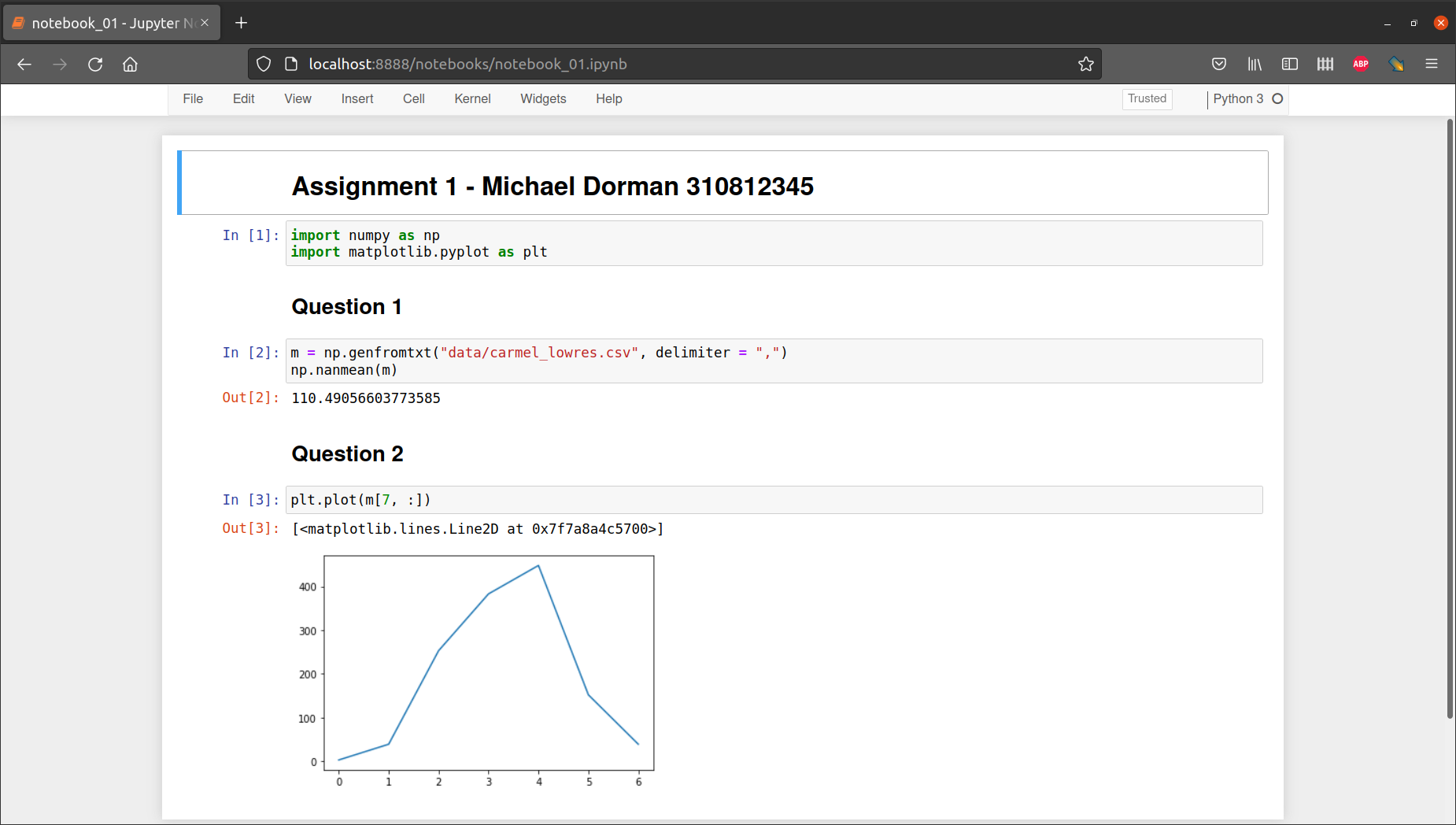
Fig. 83 Structure of .ipynb file for a submitted assignment#